With the development of the times and the continuous improvement of people's living standards, the requirements for clothing have also been continuously improved. It is not limited to warmth, durability, and new requirements have been put forward for comfort, aesthetics, and functionality. The fabric is prone to fluffing and pilling during wearing. This phenomenon not only deteriorates the appearance and feel of the fabric, but also wears the fabric and reduces the performance of the fabric.
Fabric pilling process
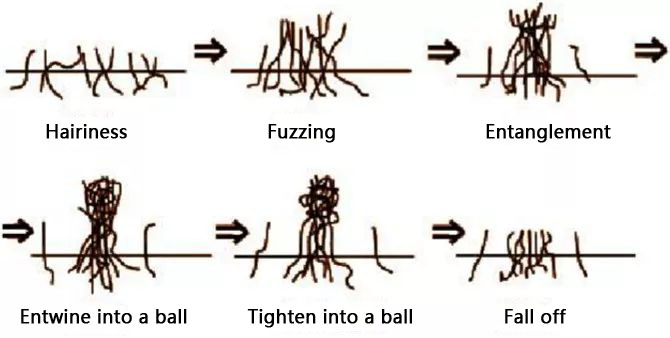
Factors Affecting Pilling
Factors affecting fabric pilling are mainly the effects of fiber properties, yarn, fabric structure, dyeing and finishing process, etc.
1. Fiber properties
Fibers with high strength, large elongation, high resistance to repeated bending, and strong wear resistance are not easy to be broken or shed when rubbed, but will further entangle with the surrounding hair clumps and hair balls to form larger balls. However, the fiber strength is low, and the formed hair balls are easy to fall off from the surface of the fabric after friction. Therefore, the fiber strength is high and easy to pill.
Short fibers are easier to pill than long fibers, and long fibers are less prone to pilling than short fibers.
The frictional resistance of long fibers in the yarn is greater than that of short fibers, and it is not easy to be drawn out from the yarn.
In the same number of fiber cross-sections, the end of the long fiber exposed to the surface of the yarn is less than that of the short fiber, and the chance of being rubbed by external force is small.
Polyester filaments have high strength and are not easy to wear and break when subjected to mechanical external force, and polyester filament fabrics are not easy to pilling.
For the same raw materials, thin fibers are easier to pill than thick fibers. The thicker the fibers, the greater the bending stiffness.
The friction between the fibers is large, the fibers are not easy to slide, and it is not easy to pilling.
-
Fiber blends are prone to pilling
Especially the blended fabrics of chemical fibers and wool, cotton, and regenerated cellulose fibers are prone to pilling, because the chemical fiber fibers are relatively strong ball fibers and are not easy to fall off.
-
Fiber cross-sectional shape
The fiber with special-shaped cross-section has high bending rigidity, is not easy to bend and entangle, and has a low probability of relative contact and friction, is not easy to pull out and entangle, and is not easy to produce pilling.
The more crimped the fiber is, the less likely the fiber is to stretch when twisting, and the fiber is easy to loosen and slip during the friction process, forming plush on the surface of the yarn. Therefore, the better the curl of the fiber, the easier it is to pilling.
2. Yarn
The main factors that affect the pilling of fabrics are yarn hairiness and wear resistance, which involve factors such as spinning method, spinning process, yarn twist, and yarn structure.
The fiber arrangement in combed yarn is relatively straight, the short fiber content is less, the fibers used are generally longer, and the yarn hairiness is less. Therefore, combed fabrics are generally not easy to pilling.
During the entire spinning process, the fibers are subject to repeated drafting and carding. If the process parameters are not set properly and the equipment is not in good condition, the fibers are easily damaged and broken during the processing process, resulting in an increase in the short pile, thus making the yarn The hairiness and hairiness increase, thereby reducing the pilling resistance of the fabric.
High twist can reduce yarn hairiness and is not easy to cause pilling, but continuous increase of twist will reduce fabric strength and affect fabric feel and style.
Changing the yarn structure can also improve the abrasion resistance of the yarn to a certain extent. In the new technology of ring spinning, siro spinning, cable spinning, compact spinning, etc. make the yarn obtain a special structure through the change of the spinning mechanism. Compared with the traditional spun yarn, the abrasion resistance and anti-pilling performance of the fabric are significantly increased.
3. Fabric structure
Fabrics with a loose structure are more prone to pilling than fabrics with a tight structure. When the fabric with a tight structure rubs against external objects, it is not easy to produce plush, and the already produced plush is not easy to slide to the surface of the fabric due to the high friction resistance between fibers, so the phenomenon of pilling can be reduced.
The fabric with flat surface is not easy to pilling, and the fabric with uneven surface is easy to pilling. Therefore, the pilling resistance of ordinary colored fabrics, ribbed fabrics, flat knitted fabrics, etc. is gradually increased.
4. Influence of dyeing and finishing process
Post-finishing has a lot to do with fabric pilling. After the yarn or fabric is dyed and finished, the pilling resistance will change greatly, which is related to dyes, auxiliaries, and dyeing and finishing process conditions.
Pilling test method
At present, the commonly used anti-pilling test methods include the circular trajectory method, the Martindale method, the pilling box method and the random tumbling method.
Circular trajectory method: AG34 Circular Locus Pilling Tester(Circular trajectory method)
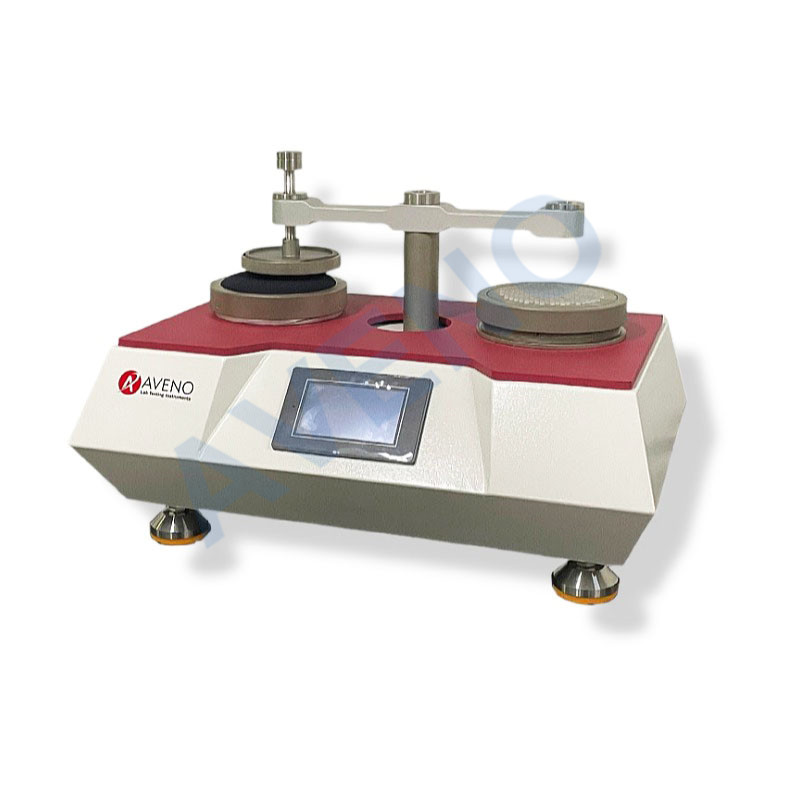

The Martindale method: AG04 Martindale Abrasion and Pilling Tester
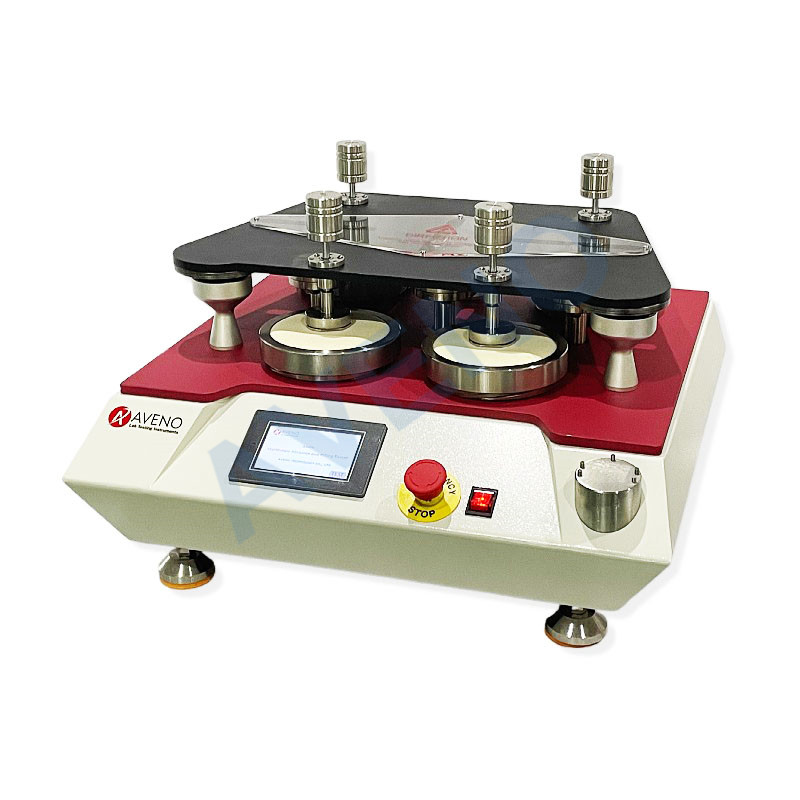

The pilling box method: AG05 ICI Pilling and Snagging Tester
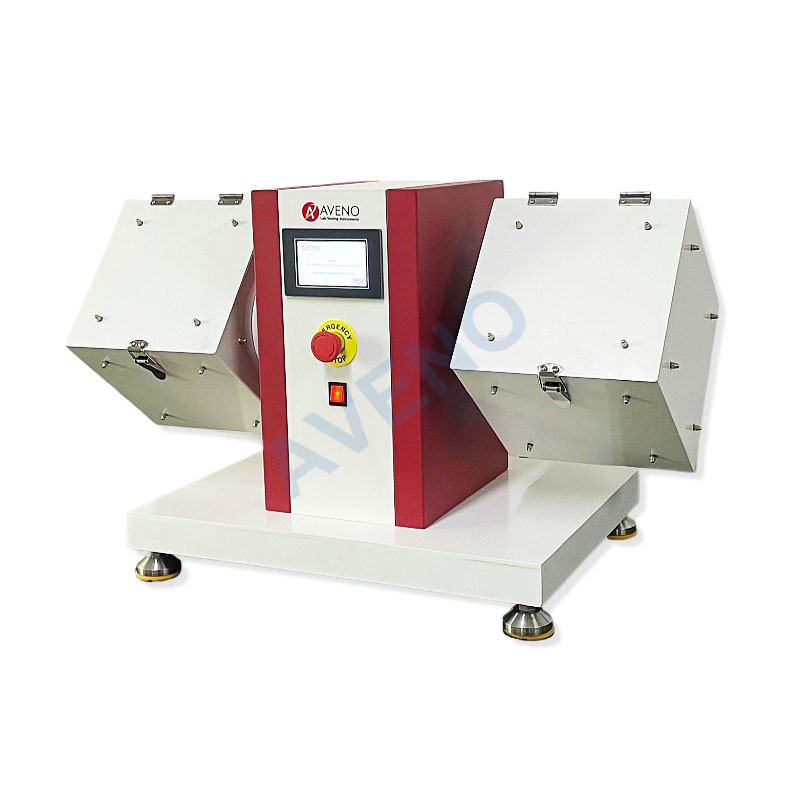

The random tumbling method: AG15 Random Tumble Pilling Tester
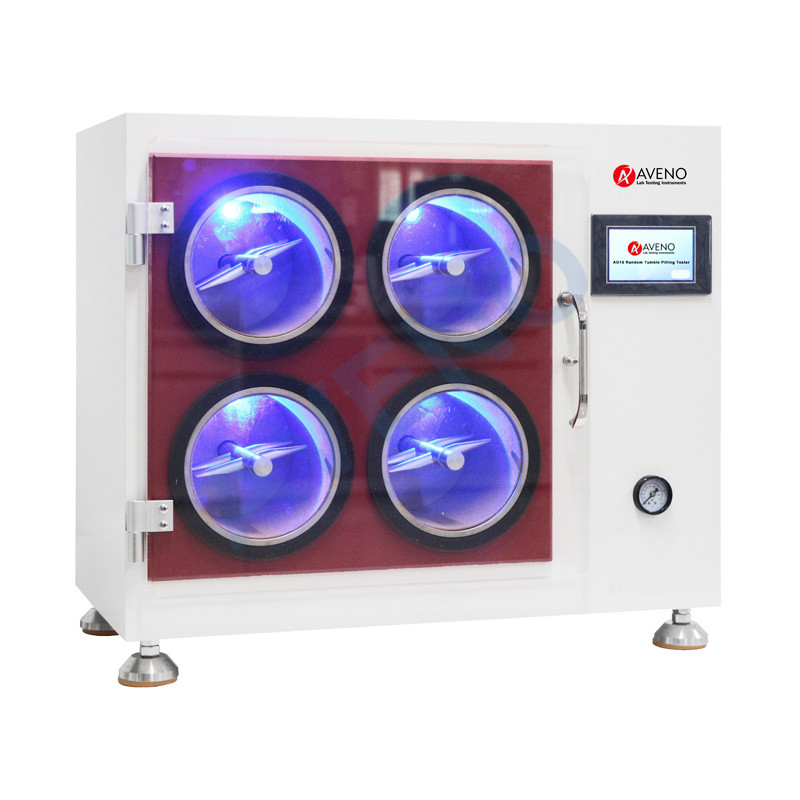

Due to different test methods, conditions, and principles, the anti-pilling performance of the same piece of fabric is quite different. The influence of different test methods on the anti-pilling level of fabrics.
There are discrepancies between the test results due to different test methods. For textile export enterprises, facing the different standards of trading countries, in the aspect of testing anti-pilling, the corresponding test method should be selected according to the use of the product and the requirements of customers. Customers have higher and higher requirements for fabrics. Testers should learn many foreign testing standards, pay attention to the testing standards required by the target, market, and exporting country in the trade contract, and conduct testing and rating strictly according to their requirements, so as to avoid failure due to ignorance of the standards. It will affect production and sales, thereby causing losses to customers and the company.
Fabrics prone to pilling
Wool and its blended fabrics:
Knitted sweaters, woolens, woolen sweaters, etc.
Chemical staple fiber and its blended fabrics:
Polyester cotton, polyester viscose, acrylic cotton, etc.
Knitting category for lightweight fabrics:
Pure cotton frame, modal, viscose, lyocell and other regenerated cellulose fiber fabrics.
denim embroidery
Contact Us Now!
Sales Dept Tel: +86 15280858852
Email: sales@avenotester.com
Skype: sales@avenotester.com
Web: www.avenotester.com



 +8615280858852
+8615280858852














 Jan 02, 2026
Jan 02, 2026





 online service
online service +8615280858852
+8615280858852
 +8615280858852
+8615280858852